Trading Technique Breaking the Reversal Bar: Understanding When to Enter with Multiple Strategies-
- What is a reversal bar?
- How to trade with the reversal bar breaking technique?
- There are other details that can improve this strategy:
- When to enter with the reversal bar technique?
- Where to put the stop loss?
- When to take profit?
The trading technique with breaking the reversal bar is one of the staples of professional traders, however if we entered all the breaks of a reversal bar our trading would certainly be negative, so it is necessary to have parameters to strengthen the technical and make it reliable and profitable.
While having a unique generic definition of a reversal bar, every successful trader has a different way of trading it.
What is the right and least risky way? It depends on your trading, the markets you follow and your risk appetite. No trading strategy is absolutely valid for all traders, everyone must find which is the right one for themselves and further shape it to their own operations.
However, the general rules remain unchanged.
What is a reversal bar?
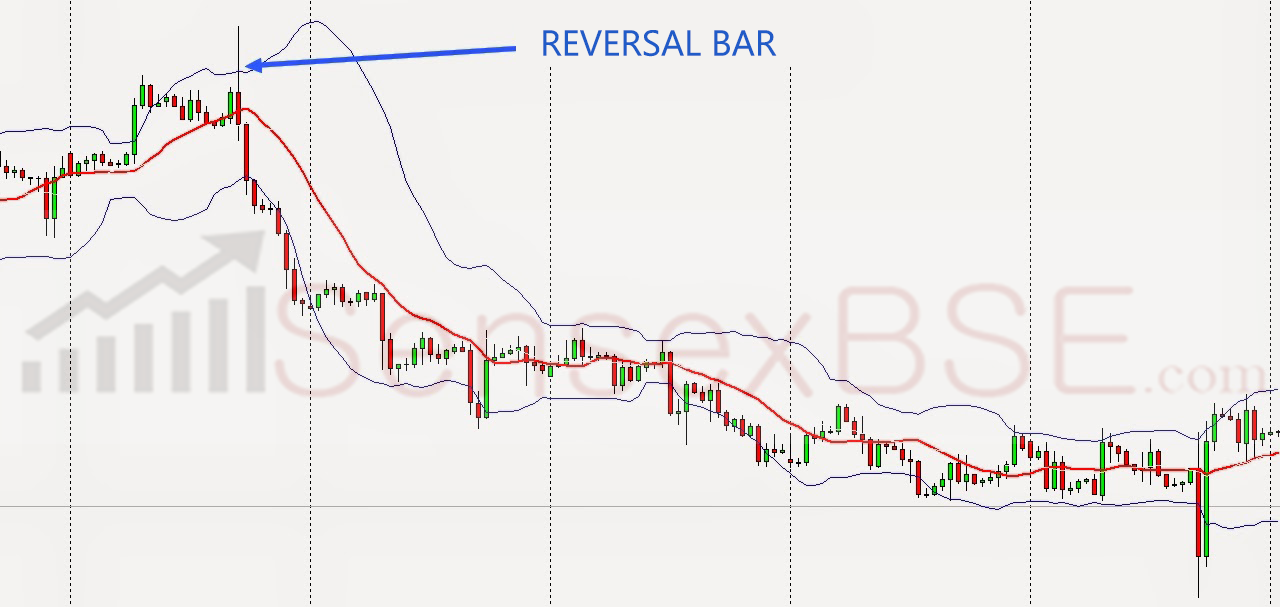
A reversal bar is a price bar that shows a possible change in the direction of the market. After a bearish trend , it is the first bullish bar ( close higher than the open) that forms after a period low. Precisely a bar that reverses the downtrend, at least temporarily.
Conversely, in a bull market , the reversal bar is the first bearish bar (close less than the open) that forms after a period high.
The market does not necessarily have to change direction after this bar. In fact, it often happens that a reversal bar becomes just a pause in the current trend, a so-called retracement .
How to trade with the reversal bar breaking technique?
In this article, however, I want to deepen the technique of breaking the reversal bar to make the strategy much stronger.
To do this I simply intersected two techniques which became a single trading strategy with the breakdown of the reversal bar.
The reverse bar – to be trusted – it must form a maximum period (or minimum) value of more than 10 bars. In his case it is 10 days, however it is a rule that we can safely apply even on intraday time frames, trying not to go below 15 minutes.
For example, in intraday trading we will look for an entry only if the reversal bar that has formed is (up to that moment) the high or low of the day or in any case more than 10 bars.
There are other details that can improve this strategy:
- the reversal bar must have a price range greater than the last 10 bars , ie the distance between the maximum and the minimum of the bar must be greater than the distance between the maximum and minimum of the last 10 bars;
- the close must be in the last quarter of the reversal bar opposite to the high or low of the period, therefore closer to the high if it is bullish or to the low if it is bearish.
This is why it is absolutely necessary to try to strengthen the signal as much as possible, whatever the trading technique you use.
When to enter with the reversal bar technique?
After having found the signals and therefore the real reliability of the reversal bar, we enter the break of the minimum of a bearish reversal bar or the maximum of a bullish reversal bar.
Sometimes, on some instruments and especially on low intraday time frames, the real break occurs only on the second crossing , so you can also decide to wait for the price to break the entry limit for the first time and then return inside the bar for then enter at the second break of the entry limit. This practice strengthens the signal, limits the risk, even if sometimes the price can start without us, but if we have a solid trading plan , it doesn’t matter, in the long run we will always be profitable.
Where to put the stop loss?
This depends on you, your risk appetite and your trading. The technical stop is usually at the low (or high) of a bullish (or bearish) reversal bar. However, you can reduce the risk by anticipating the entry on a lower time frame to have the possibility of a technical stop more suited to our needs or opting for a cash stop loss (the maximum you are willing to lose for that trade) and close in advance if the price does not go in your direction within a certain number of bars ( timed stop ).
When to take profit?
Always take profit with a part of the position after a few points based on the time frame you are trading on and let the profits run with the remaining position, trying to protect the profit with an automatic or manual trailing stop (I prefer the latter if I can follow the trade from your pc or mobile device).
There is still a lot to be said on the subject. Soon I will deepen the matter with some practical examples of trading with the technique of breaking the reversal bar .

